Adenoid Hypertrophy
Children under 5 years old are most likely to have enlarged adenoids.
Adenoid Hypertrophy
Children under 5 years old are most likely to have enlarged adenoids.
What is Adenoid Hypertrophy?
Adenoid Hypertrophy, also known as enlarged adenoids or enlarged adenoids is the abnormal growth of the adenoids. The adenoids, which are tiny masses of lymphatic tissue in the upper airway between the nose to the back of your throat, are located in the upper part of the nasal cavity. It protects the body from microbes, absorbs nutrients, regulates fluid levels, and eliminates waste products. Because of their anatomical location, the adenoids can help prevent infection by keeping germs out of the body via the nose or mouth. Children under 5 years old are most likely to have enlarged adenoids. The adenoids will shrink in size after this time and no longer play a significant role in the immune system.
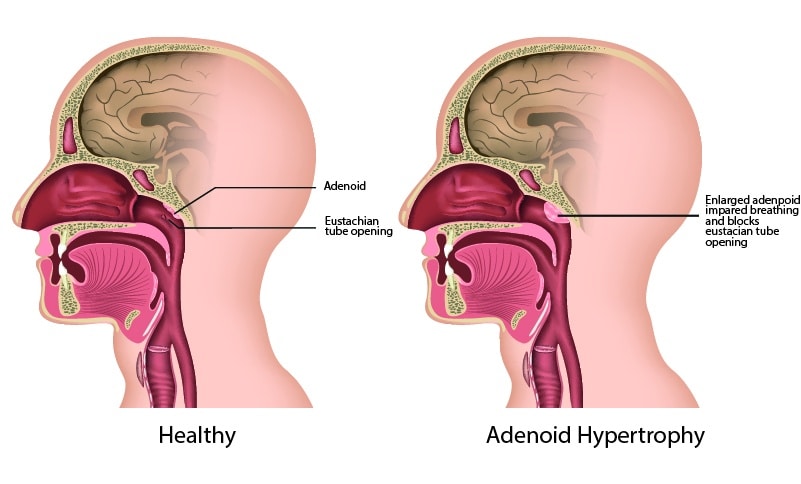
What are the Symptoms of Adenoid Hypertrophy?
A variety of symptoms can be caused by adenoid hypertrophy, which mainly affects the airways and surrounding structures. Most people will only experience mild enlargements and not be symptomatic. Nasal obstruction is a more serious condition that can lead to enlargements of greater severity. This refers to a partial or complete blockage in the nasal airway. Some of the symptoms can be:
- Mouth breathing rather than the nose.
- Bad breath
- Dry mouth
- Cracked lips
- Nasal congestion
- Nasal obstruction may also cause a blockage of the Eustachian tubes
- Ear Infection
- Cough
- Sleep Apnea
At What Age Should You Consider Removing Adenoids?
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the adenoid. It is typically performed between those under seven years of age on recommendation by your Century ENT specialist. Most often, surgery is not necessary and the adenoids shrink with age.

Treatment Options May Include:
Century ENT doctors can examine adults or children for enlarged adenoids and or tonsils; or offer treatment for recurring sinus infections.
Surgery is most commonly performed in children under the age of 7 as the adenoids shrink and are gone by age 13. If a patient does not respond to medical management, an adenoidectomy may be recommended.
